SpringBoot
1,什么是Springboot
Spring Boot可以帮助您创建可以运行的独立的,基于生产级的基于Spring的应用程序。我们对Spring平台和第三方库持固执己见的观点,这样您就可以以最小的麻烦开始使用。大多数Spring Boot应用程序只需要很少的Spring配置。
您可以使用Spring Boot创建Java应用程序,可以通过使用java -jar或更传统的战争部署来启动Java应用程序。我们还提供了运行“ spring脚本”的命令行工具。
我们的主要目标是:
为所有Spring开发提供根本上更快且可广泛访问的入门体验。
开箱即用,但由于需求开始与默认值有所出入,因此请尽快避开。
提供一系列大型项目通用的非功能性功能(例如嵌入式服务器,安全性,指标,运行状况检查和外部化配置)。
完全没有代码生成,也不需要XML配置。
2,什么是微服务
原文是 Martin Flower 于 2014 年 3 月 25 日写的《Microservices》 。
文章链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43458555/article/details/108468384
微服务
“微服务架构(Microservice Architecture)”一词在过去几年里广泛的传播,它用于描述一种设计应用程序的特别方式,作为一套独立可部署的服务。目前,这种架构方式还没有准确的定义,但是在围绕业务能力的组织、自动部署(automated deployment)、端智能(intelligence in the endpoints)、语言和数据的分散控制,却有着某种共同的特征。
“微服务(Microservices)”——只不过在满大街充斥的软件架构中的一新名词而已。尽管我们非常鄙视这样的东西,但是这玩意所描述的软件风格,越来越引起我们的注意。在过去几年里,我们发现越来越多的项目开始使用这种风格,以至于我们身边的同事在构建企业级应用时,把它理所当然的认为这是一种默认开发形式。然而,很不幸,微服务风格是什么,应该怎么开发,关于这样的理论描述却很难找到。
简而言之,微服务架构风格,就像是把一个单独的应用程序开发为一套小服务,每个小服务运行在自己的进程中,并使用轻量级机制通信,通常是 HTTP API。这些服务围绕业务能力来构建,并通过完全自动化部署机制来独立部署。这些服务使用不同的编程语言书写,以及不同数据存储技术,并保持最低限度的集中式管理。
在开始介绍微服务风格(microservice style)前,比较一下整体风格(monolithic style)是很有帮助的:一个完整应用程序(monolithic application)构建成一个单独的单元。企业级应用通常被构建成三个主要部分:客户端用户界面(由运行在客户机器上的浏览器的 HTML 页面、Javascript 组成)、数据库(由许多的表构成一个通用的、相互关联的数据管理系统)、服务端应用。服务端应用处理 HTTP 请求,执行领域逻辑(domain logic),检索并更新数据库中的数据,使用适当的 HTML 视图发送给浏览器。服务端应用是完整的 ,是一个单独的的逻辑执行。任何对系统的改变都涉及到重新构建和部署一个新版本的服务端应用程序。
这样的整体服务(monolithic server)是一种构建系统很自然的方式。虽然你可以利用开发语基础特性把应用程序划分成类、函数、命名空间,但所有你处理请求的逻辑都运行在一个单独的进程中。在某些场景中,开发者可以在的笔计本上开发、测试应用,然后利用部署通道来保证经过正常测试的变更,发布到产品中。你也可以使用横向扩展,通过负载均衡将多个应用部署到多台服务器上。
整体应用程序(Monolithic applications)相当成功,但是越来越多的人感觉到有点不妥,特别是在云中部署时。变更发布周期被绑定了——只是变更应用程序的一小部分,却要求整个重新构建和部署。随着时间的推移,很难再保持一个好的模块化结构,使得一个模块的变更很难不影响到其它模块。扩展就需要整个应用程序的扩展,而不能进行部分扩展。
这导致了微服务架构风格(microservice architectural style)的出现:把应用程序构建为一套服务。事实是,服务可以独立部署和扩展,每个服务提供了一个坚实的模块边界,甚至不同的服务可以用不同的编程语言编写。它们可以被不同的团队管理。
我们必须说,微服务风格不是什么新东西,它至少可以追溯到 Unix 的设计原则。但是并没有太多人考虑微服务架构,如果他们用了,那么很多软件都会更好。
微服务风格的特性
微服务风格并没有一个正式的定义,但我们可以尝试描述一下微服务风格所具有的共同特点。并不是所有的微服务风格都要具有所有的特性,但我们期望常见的微服务都应该有这些特性。我们的意图是尝试描述我们工作中或者在其它我们了解的组件中所理解的微服务。特别是,我们不依赖于那些已经明确过的定义。
组件化(Componentization )与服务(Services)
当我们谈论组件时,可能会陷入一个困境——什么是组件。我们的定义是,组件(component)是一个可独立替换和升级的软件单元。
微服务架构(Microservice architectures)会使用库(libraries),但组件化软件的主要方式是把它拆分成服务。我们把库(libraries)定义为组件,这些组件被链接到程序,并通过内存中函数调用(in-memory function calls)来调用,而服务(services )是进程外组件(out-of-process components),他们利用某个机制通信,比如 WebService 请求,或远程过程调用(remote procedure call)。组件和服务在很多面向对象编程中是不同的概念。
把服务当成组件(而不是组件库)的一个主要原因是,服务可以独立部署。如果你的应用程序是由一个单独进程中的很多库组成,那么对任何一个组件的改变都将导致必须重新部署整个应用程序。但是如果你把应用程序拆分成很多服务,那你只需要重新部署那个改变的服务。当然,这也不是绝对的,有些服务会改变导致协调的服务接口,但是一个好的微服务架构的目标就是通过在服务契约(service contracts)中解耦服务的边界和进化机制来避免这些。
另一个考虑是,把服务当组件将拥有更清晰的组件接口。大多数开发语言都没有一个良好的机制来定义一个发布的接口(Published Interface)。发布的接口是指一个类向外公开的成员,比如 Java 中的声明为 Public 的成员,C# 中声明为非 Internal 的成员。通常只有在文档和规范中会说明,这是为了让避免客户端破坏组件的封装性,阻止组件间紧耦合。服务通过使用公开远程调用机制可以很容易避免这些。
像这样使用服务也有不足之处。远程调用比进制内调用更消耗资源,因此远程 API 需要粗粒度(coarser-grained),但这会比较难使用。如果你需要调整组件间的职责分配,当跨越进程边界时,这样做将会很难。
一个可能是,我们看到,服务可以映射到运行时进程(runtime processes)上,但也只是一个可能。服务可以由多个进程组成,它们会同时开发和部署,例如一个应用程序进程和一个只能由这个服务使用的数据库。
3,创建一个SpringBoot项目
方式一(不推荐)
可以通过官方的SpringBoot项目生成器https://start.spring.io/生成项目,然后使用IDEA导入zip包
方式二:
IDEA内部已经集成了https://start.spring.io/网站,可以在IDEA中直接创建。
4,SpringBoot自动装配原理
核心依赖
如果我们想要查看SpringBoot的核心依赖,需要找到pom.xml文件,在pom.xml配置文件中寻找maven的父工程,顶级工程spring-boot-dependencies内部定义了足足两千多行的依赖
所以在我们创建SpringBoot时不需要指定个个详细的依赖,因为在顶级父工程中制定了版本
各个版本的SpringBoot所指定的依赖版本不同,不过都可以在官方文档中查看,2.4.5的SpringBoot可以在网址:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/appendix-dependency-versions.html#dependency-versions-coordinates中查看
启动器
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId > </dependency >
启动器:也就是SpringBoot的启动场景
SpringBoot将启动器封装起来,内部包含了该启动器的所有依赖
如果我们想要添加别的启动场景,我们就可以直接添加启动器即可,SprintBoot会自动帮我们导入所需场景的依赖
需要什么功能,直接导入启动器(spring-boot-starter-XXX)即可。
自动装配
帮助文档
CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38526573/article/details/107084943
知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/123343325,https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/95217578(这个挺好)
博客园:https://www.cnblogs.com/hhcode520/p/9450933.html(不错)
SpringBoot完美的诠释了什么叫JavaConfig配置Spring
注解
@SpringBootApplication——(标注该类是一个SpringBoot的应用)
@SpringBootConfiguration——(SpringBoot的配置)
@Configuration——(Spring的JavaConfig的配置类)
@ComponentScan——(帮助我们去寻找指定包下的@Component等等标签注册到IOC容器当中)
@EnableAutoConfiguration ——(重点:启动自动JavaConfig配置类)
@AutoConfigurationPackage——(自动扫描@SpringBootApplication注解包下所有组件并注册)
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
关键配置类
关键方法
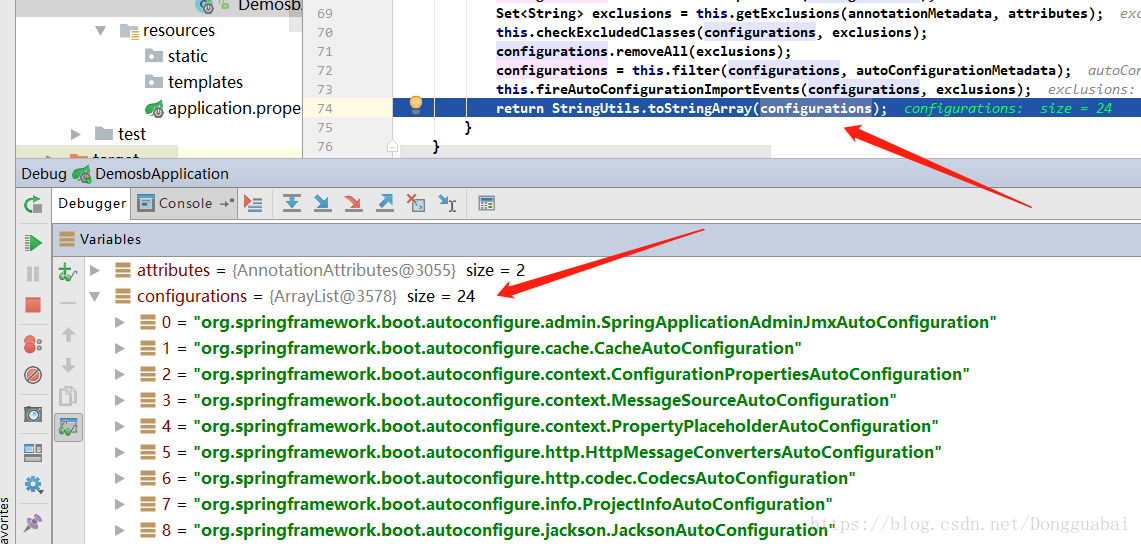
图片链接地址:http://assets.processon.com/chart_image/6093bca41e0853762874bea6.png
总结 当我们的SpringBoot项目启动的时候,会先导入AutoConfigurationImportSelector,这个类会帮我们选择所有候选的配置,我们需要导入的配置都是SpringBoot帮我们写好的一个一个的配置类,那么这些配置类的位置,存在与META-INF/spring.factories文件中,通过这个文件,Spring可以找到这些配置类的位置,于是去加载其中的配置。
SpringBoot所有的自动配置会在启动时去扫描并加载,META-INF/spring.factories文件装载了所有的自动配置类(JavaConfig类),但是并不是所有的自动配置类都会生效,装配,只有项目有对应的启动器时(也就是加入了对应的依赖如:web依赖),对应的自动装配类才会生效,具体实现是:@ConditionalOnXXX 注解
SpringBoot在启动时,会在类的路径下META-INF/spring.factories文件获取指定的值
通过值将指定的自动配置类导入至IOC容器,那么自动配置就会生效,帮助我们进行配置
整个JavaEE,解救方案和自动配置的东西都在spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.4.5.jar下
它会把所有需要导入的组件,以类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器中
spring.factories文件存在非常多的XXXAutoConfiguration的文件(@Bean),这些类就是自动装配类,存在这个场景需要的所有组件,并自动装配(JavaConfig配置类)
5,多环境多配置
优先级
#application.properties 优先级从高到低,application.yml文件优先级也一样
1、-- 项目根目录config文件夹里面(优先级最高)
2、–项目根目录
3、-- src/main/resources/config/文件夹里面
4、-- src/main/resources/
1-4优先级从高到低,优先级高的配置内容会覆盖优先级低的配置内容
如何选择配置文件
在不同的环境下需要选择不同的配置文件(生产环境,测试环境)
那么我们应该如何选择配置文件呢
我们只需要在application.yaml加入
1 2 3 spring: profiles: active: dev
其中dev是其他配置文件的后缀名(后缀名可以看作配置文件的别名)
6,SpringBoot自动装配再理解
为什么我们SpringBoot的配置文件application.yaml可以修改SpringBoot原有配置呢
如:可以修改端口
原理
背后的原理其实就是yaml去给我们的JavaConfig类属性赋值
以字符编码配置类举例
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.HttpEncodingAutoConfiguration,\
通过注解@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
去指定我们的JavaConfig配置类,也就是ServerProperties类
我们点开这个类来看一看
我们可以看到一个非常熟悉的注解@ConfigurationProperties
该注解的功能就是去yaml配置文件中去寻找server的属性并通过server以下的属性给该类的属性赋值
举例
如:现在我们想给prot属性赋值
那么我需要再yaml配置文件中去写即可
7,@Conditional注解
@Conditional是Spring4新提供的注解,它的作用是按照一定的条件进行判断,满足条件给容器注册bean。
8,WEB开发
处理静态资源
在JavaConfig配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration.java类的addResourceHandlers添加资源处理器方法中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 protected void addResourceHandlers (ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) super .addResourceHandlers(registry); if (!this .resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) { logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled" ); return ; } ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); addResourceHandler(registry, "/webjars/**" , "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/" ); addResourceHandler(registry, this .mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (registration) -> { registration.addResourceLocations(this .resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()); if (servletContext != null ) { registration.addResourceLocations(new ServletContextResource(servletContext, SERVLET_LOCATION)); } }); }
第一步判断我们是否自定义配置了类静态资源路径 if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings())
如果配置了则直接返回
然后它将静态资源路径/META-INF/resources/webjars/缩减成了路径/webjars/**
也就是将静态资源请求地址从原先的localhost:8080/META-INF/resources/webjars/**变成了
localhost:8080/webjars/**
哪会有什么静态资源会放在/META-INF/resources/webjars/下呢
以jquery举例(这里我们使用webjars导入jquery,而不是之前的直接导入js文件)
现在我们去寻找jquery.js不需要写全路径,而是写http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.js
因为/webjars已经代替了/META-INF/resources/webjars/
这是jar的静态资源
那我们项目当中的静态资源应该放在那里呢
在Resources类中就可以看到我们的静态资源可以放在那了
所以我们的静态资源可以放在"classpath:/resources/", “classpath:/static/”, "classpath:/public/"目录
优先级
resources=>static=>public
9,模板引擎
Thymeleaf模板引擎是SpringBoot推荐的模板引擎
(一)Thymeleaf 是个什么?
简单说, Thymeleaf 是一个跟 Velocity、FreeMarker 类似的模板引擎,它可以完全替代 JSP 。相较与其他的模板引擎,它有如下三个极吸引人的特点:
1.Thymeleaf 在有网络和无网络的环境下皆可运行,即它可以让美工在浏览器查看页面的静态效果,也可以让程序员在服务器查看带数据的动态页面效果。这是由于它支持 html 原型,然后在 html 标签里增加额外的属性来达到模板+数据的展示方式。浏览器解释 html 时会忽略未定义的标签属性,所以 thymeleaf 的模板可以静态地运行;当有数据返回到页面时,Thymeleaf 标签会动态地替换掉静态内容,使页面动态显示。
2.Thymeleaf 开箱即用的特性。它提供标准和spring标准两种方言,可以直接套用模板实现JSTL、 OGNL表达式效果,避免每天套模板、该jstl、改标签的困扰。同时开发人员也可以扩展和创建自定义的方言。
3. Thymeleaf 提供spring标准方言和一个与 SpringMVC 完美集成的可选模块,可以快速的实现表单绑定、属性编辑器、国际化等功能。
使用Thymeleaf 前提 官方文档:https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
在SpringBoot项目的pom文件中导入Thymeleaf
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId > </dependency >
在我们创建的所有html文件中加入约束/命名空间
1 <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" >
使用 使用和jsp相似
通过model携带数据
返回字符串,经过视图解析器解析
指定页面,通过Thymeleaf语法接收数据
查看配置类
我们可以看一下Thymeleaf的JavaConfig配置类ThymeleafProperties
可以看到Thymeleaf会去扫描资源包下的templates路径,然后拼接.html后缀
所以我们的所有页面必须放在templates路径下,同时页面以html后缀结尾
这里可以深刻体会到约定大于配置
语法
简单表达式:
变量表达式: ${...}
选择变量表达式: *{...}
消息表达: #{...}
链接URL表达式: @{...}
片段表达式: ~{...}
文字
文本文字:'one text','Another one!',…
数字文字:0,34,3.0,12.3,…
布尔文字:true,false
空文字: null
文字标记:one,sometext,main,…
文字操作:
字符串串联: +
文字替换: |The name is ${name}|
算术运算:
二元运算符:+,-,*,/,%
减号(一元运算符): -
布尔运算:
二元运算符:and,or
布尔否定(一元运算符): !,not
比较和平等:
比较:>,<,>=,<=(gt,lt,ge,le)
等号运算符:==,!=(eq,ne)
条件运算符:
如果-则: (if) ? (then)
如果-则-否则: (if) ? (then) : (else)
默认: (value) ?: (defaultvalue)
10,扩展SpringMVC配置
在SpringBoot自定义设置我们的SpringMVC
文档地址:https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/spring-boot-features.html#boot-features-spring-mvc
我们可以先看自动配置视图解析
如果我们要自定义视图解析器的话,可以先看官方默认的视图解析器ContentNegotiatingViewResolver是怎么写的
官方的视图解析器实现了ViewResolver接口
ContentNegotiatingViewResolver实现了ViewResolver接口的resolveViewName方法
getCandidateViews 得到候选视图
getBestView 得到最好视图
自定义视图解析器
那么我们自定义的视图解析器需要实现ViewResolver接口并且实现了ViewResolver接口的resolveViewName方法
最后将自定义的视图解析器注册到IOC容器当中
关于注解@EnableWebMvc
在官方文档我们可以看到这样一句话
1 2 3 4 If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more [MVC customizations](interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own `@Configuration` class of type `WebMvcConfigurer` but **without** `@EnableWebMvc` 如果要保留这些Spring Boot MVC定制并进行更多的MVC定制(拦截器,格式化程序,视图控制器和其他功能),则可以添加自己@Configuration的注解,同时实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,但不添加 @EnableWebMvc注解。
为什么我们扩展配置类的时候不能添加 @EnableWebMvc注解呢
官方是这样解释的
1 2 3 4 If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with @EnableWebMvc, or alternatively add your own @Configuration-annotated DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration as described in the Javadoc of @EnableWebMvc. 如果你想利用Spring MVC中的完全控制,你可以添加自己配置类添加@Configuration注解和@EnableWebMvc,或者添加自己的@Configuration-annotatedDelegatingWebMvcConfiguration中的Javadoc中所述@EnableWebMvc。
所以一旦我们加上@EnableWebMvc注解我们的配置类就会完全接管MVC配置,官方的自动配置类就会失效
那SpringBoot是怎么实现的呢,看看源码!
源码分析
1,先看看注解@EnableWebMvc
该注解导入了一个DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration类
看看DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration类
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration类继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport类
好的,注解@EnableWebMvc先到这里,不过要记住WebMvcConfigurationSupport类
2,再来看看SpringBoot官方的Web配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration类
在最上方我们看到了
1 @ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
之前我们一再强调@ConditionalXXX系列注解的重要性
现在我们就知道了原理
只有容器中不存在WebMvcConfigurationSupport类那么WebMvcAutoConfiguration类才会生效,
那么再看@EnableWebMvc注解,它内部继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport类
也就是现在IOC容器内存在了WebMvcConfigurationSupport类,
所以官方的Web配置类WebMvcAutoConfiguration类不会生效
11,练习
1,国际化
我们先定义一个页面的语言包内部包含中英文
然后再SpringBoot配置文件中配置语言包
1 2 spring.messages.basename =i18n/login
然后我们自定义配置文件的话我们可以参考官方的国际化包AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class MyLocaleResolver implements LocaleResolver @Override public Locale resolveLocale (HttpServletRequest request) String l = request.getParameter("l" ); Locale locale = Locale.getDefault(); if (l!=null ){ String[] s = l.split("_" ); locale =new Locale(s[0 ],s[1 ]); } return locale; } @Override public void setLocale (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Locale locale) } }
最后将我们自己配置的类装配到扩展配置类中
@Bean
注意方法名必须是localeResolver
2,拦截器
实现连接器接口HandlerInterceptor
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public class Interceptor implements HandlerInterceptor @Override public boolean preHandle (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception HttpSession session = request.getSession(); String user = (String) session.getAttribute("user" ); if (user==null ){ response.sendRedirect("/index.html" ); return false ; } return true ; } }
将自己的拦截器添加到自己的扩展配置类中
扩展配置类重写addInterceptors方法
1 2 3 4 5 @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) registry.addInterceptor(new Interceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**" ).excludePathPatterns("/user/login" ,"/index.html" ); }
new一个自己的拦截器,拦截"/**“的所有请求,排除”/user/login","/index.html"请求
12,数据库的连接与配置
1,JDBC
1,1 创建SpringBoot项目时勾选JDBC和Mysql数据库的支持
1,2 在yaml配置文件中配置数据库的用户名,密码,连接地址,Driver
1 2 3 4 5 6 spring: datasource: username: root password: root url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSl=true driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
1,3 如何使用
在SpringBoot中使用JDBC不需要再像之前的JavaEE阶段从获取连接 connection,预编译sql语句PreparedStatement ,结果集ResultSet等等
而是使用SpringBoot集成的模板XXXTemplate
JDBC的模板是jdbcTemplate,使用它可以直接执行sql语句,传入值集合,也可以预编译
2,集成Druid
文档:https://github.com/alibaba/druid/wiki/Druid连接池介绍
Druid 简介
更新时间: 2020-01-18
Apache Druid 是一个分布式内存实时分析系统,用于解决如何在大规模数据集下进行快速的、交互式的查询和分析的问题。Apache Druid 由 Metamarkets 公司(一家为在线媒体或广告公司提供数据分析服务的公司)开发,在2019年春季被捐献给 Apache 软件基金会。
基本特点
Apache Druid 具有以下特点:
亚秒级 OLAP 查询,包括多维过滤、Ad-hoc 的属性分组、快速聚合数据等等。
实时的数据消费,真正做到数据摄入实时、查询结果实时。
高效的多租户能力,最高可以做到几千用户同时在线查询。
扩展性强,支持 PB 级数据、千亿级事件快速处理,支持每秒数千查询并发。
极高的高可用保障,支持滚动升级。
应用场景
实时数据分析是 Apache Druid 最典型的使用场景。该场景涵盖的面很广,例如:
这些场景的特点都是拥有大量的数据,且对数据查询的时延要求非常高。在实时指标监控中,系统问题需要在出现的一刻被检测到并被及时给出报警。在推荐模型中,用户行为数据需要实时采集,并及时反馈到推荐系统中。用户几次点击之后系统就能够识别其搜索意图,并在之后的搜索中推荐更合理的结果。
使用Druid
1,首先在SpringBoot项目中导入Druid的starter,如果我们Druid配置了log4j的日志打,还需要加入log4j的依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>1.1.10</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/log4j/log4j --> <dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency>
2,通过yaml配置Druid
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 spring: datasource: name: druidDataSource type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource druid: driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSl=true username: root password: root filters: stat,wall,log4j max-active: 100 initial-size: 1 max-wait: 60000 min-idle: 1 time-between-eviction-runs-millis: 60000 min-evictable-idle-time-millis: 300000 validation-query: select 'x' test-while-idle: true test-on-borrow: false test-on-return: false pool-prepared-statements: true max-pool-prepared-statement-per-connection-size: 20 use-global-data-source-stat: true stat-view-servlet: login-username: admin login-password: admin
3,如果报了图片的错误
则需要在资源包下添加名为:log4j.properties log4j的properties配置文件
并将以下内容复制进去
1 2 3 4 log4j.rootLogger =DEBUG, stdout log4j.appender.stdout =org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.stdout.layout =org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern =%5p [%t] - %m%n
3,整合Mybatis框架
Mybatis框架可以和Druid共存,只需要分别配置即可
导入依赖
这是Maven的mybatis自己写的依赖,所以命名是spring-boot-starter在后面,官方是以spring-boot-starter开头的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependency > <groupId > org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId > <artifactId > mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.1.4</version > </dependency >
配置Mybatis
编写Mapper接口
值得注意的是我们需要在接口上加上@Repository注解将其交给IOC容器管理
@Mapper注解的的作用
1:为了把mapper这个DAO交給Spring管理 http://412887952-qq-com.iteye.com/blog/2392672
2:为了不再写mapper映射文件 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39666581/article/details/103899495
3:为了给mapper接口 自动根据一个添加@Mapper注解的接口生成一个实现类 http://www.tianshouzhi.com/api/tutorials/mapstruct/292
但是在一个dao层接口写上@Mapper明显比较繁琐,那么在工程较大时,可以在SpringBoot的主启动类加上@MapperScan() 注解 ,只要在注解内部写上dao层接口的路径,就会自动扫描并注册
可参考:https://www.iteye.com/blog/412887952-qq-com-2392672
13,SpringSecurity
Spring Security 是 Spring 家族中的一个安全管理框架,实际上,在 Spring Boot 出现之前,Spring Security 就已经发展了多年了,但是使用的并不多,安全管理这个领域,一直是 Shiro 的天下。
相对于 Shiro,在 SSM/SSH 中整合 Spring Security 都是比较麻烦的操作,所以,Spring Security 虽然功能比 Shiro 强大,但是使用反而没有 Shiro 多(Shiro 虽然功能没有 Spring Security 多,但是对于大部分项目而言,Shiro 也够用了)。
自从有了 Spring Boot 之后,Spring Boot 对于 Spring Security 提供了 自动化配置方案,可以零配置使用 Spring Security。
因此,一般来说,常见的安全管理技术栈的组合是这样的:
SSM + Shiro
Spring Boot/Spring Cloud + Spring Security
注意,这只是一个推荐的组合而已,如果单纯从技术上来说,无论怎么组合,都是可以运行的。
**帮助文档:**https://www.cnblogs.com/lenve/p/11242055.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/felordcn/p/12142549.html
使用SpringSecurity
在pom配置文件中导入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId > <version > 2.4.5</version > </dependency >
当我们添加依赖后,Security会直接生效
访问请求时,会要求我们登录
默认的用户名是user ,而密码会在每一次启动项目时生成
配置文件指定用户名和密码
我们也可以自定义密码和用户名,这样就不会每一次靠Security生成
在yaml配置文件中指定用户名和密码
Java配置文件指定用户名和密码
首先我们创建一个JavaConfig的配置类,将配置类继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类
并且在配置类上方加上@EnableWebSecurity注解,开启web安全
@EnableWebSecurity注解内部有一个@Configuration注解了,所以不需要在加了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @EnableWebSecurity public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/" ,"/toLogin" ).permitAll() .antMatchers("/views/1/**" ).hasRole("1" ) .antMatchers("/views/2/**" ).hasRole("2" ) .antMatchers("/views/3/**" ).hasRole("3" ); http.formLogin(); } @Override protected void configure (AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder()) .withUser("admin" ).password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123" )).roles("1" ,"2" ,"3" ) .and().withUser("xpp011" ).password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123" )).roles("1" ); } }
从数据库得到用户认证,参考文档 :https://blog.csdn.net/BLU_111/article/details/110727891
注意WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类有很多的configure重载方法,它们分别是
2.1 认证管理器配置方法
void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) 用来配置认证管理器AuthenticationManager。说白了就是所有 UserDetails 相关的它都管,包含 PasswordEncoder 密码机。如果你不清楚可以通过 Spring Security 中的 UserDetail 进行了解。本文对 AuthenticationManager 不做具体分析讲解,后面会有专门的文章来讲这个东西 。 可通过 Spring Security 实战系列 进行学习。
2.2 核心过滤器配置方法
void configure(WebSecurity web) 用来配置 WebSecurity 。而 WebSecurity 是基于 Servlet Filter 用来配置 springSecurityFilterChain 。而 springSecurityFilterChain 又被委托给了 Spring Security 核心过滤器 Bean DelegatingFilterProxy 。 相关逻辑你可以在 WebSecurityConfiguration 中找到。我们一般不会过多来自定义 WebSecurity , 使用较多的使其ignoring() 方法用来忽略 Spring Security 对静态资源的控制。
2.3 安全过滤器链配置方法
void configure(HttpSecurity http) 这个是我们使用最多的,用来配置 HttpSecurity 。 HttpSecurity 用于构建一个安全过滤器链 SecurityFilterChain 。SecurityFilterChain 最终被注入核心过滤器 。 HttpSecurity 有许多我们需要的配置。我们可以通过它来进行自定义安全访问策略。所以我们单独开一章来讲解这个东西。
13.1,SpringSecurity和thymeleaf整合
文档:https://github.com/thymeleaf/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/articles/springsecurity.html
导入maven依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependency > <groupId > org.thymeleaf.extras</groupId > <artifactId > thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity5</artifactId > <version > 3.0.4.RELEASE</version > </dependency >
在html文件导入正确的约束xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security"是官方推荐的命名空间
1 2 <html lang ="en" xmlns:th ="http://www.thymeleaf.org" xmlns:sec ="http://www.thymeleaf.org/extras/spring-security" >
用来判断是否登录验证
登录页定制和记住我
定制首页 只需在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中加入
1 2 3 4 5 http.formLogin().loginPage("/toLogin" ) .loginProcessingUrl("/login" ) .usernameParameter("username" ) .passwordParameter("password" ) .defaultSuccessUrl("/" );
登录退出
1 2 3 http.logout() .logoutUrl("/logout" ) .logoutSuccessUrl("/" );
注意在登录请求 /toLogin,/login和登录退出请求 /logout均为post请求 ,a标签的href为get,所以不要使用a标签请求 ,不然会导致404的情况
记住我
1 2 3 http.rememberMe() .rememberMeParameter("remember" ) .tokenValiditySeconds(60 *60 *24 *7 );
关于数据库保存cookie的token值
参考:https://www.jb51.net/article/175334.htm
建议以后项目实现一下,有意义
14,Shiro
简介 Apache Shiro是一个强大且易用的Java安全框架,执行身份验证、授权、密码和会话管理。使用Shiro的易于理解的API,您可以快速、轻松地获得任何应用程序,从最小的移动应用程序到最大的网络和企业应用程序。
**官网:**https://shiro.apache.org/index.html
**帮助文档:**https://www.w3cschool.cn/shiro/co4m1if2.html (值得一看)
Authentication :身份认证 / 登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;Authorization :授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限;即判断用户是否能做事情,常见的如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色。或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限;Session Management :会话管理,即用户登录后就是一次会话,在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中;会话可以是普通 JavaSE 环境的,也可以是如 Web 环境的;Cryptography :加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库,而不是明文存储;Web Support :Web 支持,可以非常容易的集成到 Web 环境;Caching :缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息、拥有的角色 / 权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率;Concurrency :shiro 支持多线程应用的并发验证,即如在一个线程中开启另一个线程,能把权限自动传播过去;Testing :提供测试支持;Run As :允许一个用户假装为另一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;Remember Me :记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了。
记住一点,Shiro 不会去维护用户、维护权限;这些需要我们自己去设计 / 提供;然后通过相应的接口注入给 Shiro 即可。
架构
接下来我们分别从外部和内部来看看 Shiro 的架构,对于一个好的框架,从外部来看应该具有非常简单易于使用的 API,且 API 契约明确;从内部来看的话,其应该有一个可扩展的架构,即非常容易插入用户自定义实现,因为任何框架都不能满足所有需求。
首先,我们从外部来看 Shiro 吧,即从应用程序角度的来观察如何使用 Shiro 完成工作。如下图:
可以看到:应用代码直接交互的对象是 Subject,也就是说 Shiro 的对外 API 核心就是 Subject;其每个 API 的含义:
Subject :主体,代表了当前 “用户”,这个用户不一定是一个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是 Subject,如网络爬虫,机器人等;即一个抽象概念;所有 Subject 都绑定到 SecurityManager,与 Subject 的所有交互都会委托给 SecurityManager;可以把 Subject 认为是一个门面;SecurityManager 才是实际的执行者;
SecurityManager :安全管理器;即所有与安全有关的操作都会与 SecurityManager 交互;且它管理着所有 Subject;可以看出它是 Shiro 的核心,它负责与后边介绍的其他组件进行交互,如果学习过 SpringMVC,你可以把它看成 DispatcherServlet 前端控制器;
Realm :域,Shiro 从从 Realm 获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说 SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从 Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法;也需要从 Realm 得到用户相应的角色 / 权限进行验证用户是否能进行操作;可以把 Realm 看成 DataSource,即安全数据源。
也就是说对于我们而言,最简单的一个 Shiro 应用:
应用代码通过 Subject 来进行认证和授权,而 Subject 又委托给 SecurityManager;
我们需要给 Shiro 的 SecurityManager 注入 Realm,从而让 SecurityManager 能得到合法的用户及其权限进行判断。
从以上也可以看出,Shiro 不提供维护用户 / 权限,而是通过 Realm 让开发人员自己注入。
接下来我们来从 Shiro 内部来看下 Shiro 的架构,如下图所示:
Subject :主体,可以看到主体可以是任何可以与应用交互的 “用户”;SecurityManager :相当于 SpringMVC 中的 DispatcherServlet 或者 Struts2 中的 FilterDispatcher;是 Shiro 的心脏;所有具体的交互都通过 SecurityManager 进行控制;它管理着所有 Subject、且负责进行认证和授权、及会话、缓存的管理。Authenticator :认证器,负责主体认证的,这是一个扩展点,如果用户觉得 Shiro 默认的不好,可以自定义实现;其需要认证策略(Authentication Strategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;Authrizer :授权器,或者访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的哪些功能;Realm :可以有 1 个或多个 Realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的;可以是 JDBC 实现,也可以是 LDAP 实现,或者内存实现等等;由用户提供;注意:Shiro 不知道你的用户 / 权限存储在哪及以何种格式存储;所以我们一般在应用中都需要实现自己的 Realm;SessionManager :如果写过 Servlet 就应该知道 Session 的概念,Session 呢需要有人去管理它的生命周期,这个组件就是 SessionManager;而 Shiro 并不仅仅可以用在 Web 环境,也可以用在如普通的 JavaSE 环境、EJB 等环境;所以呢,Shiro 就抽象了一个自己的 Session 来管理主体与应用之间交互的数据;这样的话,比如我们在 Web 环境用,刚开始是一台 Web 服务器;接着又上了台 EJB 服务器;这时想把两台服务器的会话数据放到一个地方,这个时候就可以实现自己的分布式会话(如把数据放到 Memcached 服务器);SessionDAO :DAO 大家都用过,数据访问对象,用于会话的 CRUD,比如我们想把 Session 保存到数据库,那么可以实现自己的 SessionDAO,通过如 JDBC 写到数据库;比如想把 Session 放到 Memcached 中,可以实现自己的 Memcached SessionDAO;另外 SessionDAO 中可以使用 Cache 进行缓存,以提高性能;CacheManager :缓存控制器,来管理如用户、角色、权限等的缓存的;因为这些数据基本上很少去改变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能Cryptography :密码模块,Shiro 提供了一些常见的加密组件用于如密码加密 / 解密的。
使用Shiro
首先在pom配置文件中导入Shiro依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.shiro</groupId > <artifactId > shiro-spring-boot-web-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.7.1</version > </dependency >
自定义Shiro配置类 MyShiroConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 @Configuration public class MyShiroConfig @Bean("shiroFilterFactoryBean") public ShiroFilterFactoryBean ShiroFilterFactoryBean (@Qualifier("SecurityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean=new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); factoryBean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager); Map<String, String> filterMap=new LinkedHashMap<>(); filterMap.put("/add" ,"perms[user:add]" ); filterMap.put("/update" ,"perms[user:update]" ); filterMap.put("/" ,"anon" ); factoryBean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap); factoryBean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin" ); factoryBean.setUnauthorizedUrl("toUnauthorized" ); return factoryBean; } @Bean("SecurityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager DefaultWebSecurityManager (@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm) DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); return securityManager; } @Bean public UserRealm userRealm () return new UserRealm(); } @Bean public ShiroDialect shiroDialect () return new ShiroDialect(); } }
自定义的类需要三个类 分别是
ShiroFilterFactoryBean
它是Shiro的过滤器,/Filter工厂,设置对应的过滤条件和跳转条件
anon: 无需认证就可以访问
authc:必须通过认证才能访问
user:必须拥有记住我功能访问
perms:拥有某个资源访问权限才能访问
role: 拥有某个角色权限才能访问
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 - `DefaultWebSecurityManager` - 安全管理器 它负责所具体的交互,比如,身份认证,授权,控制缓存等,都由他调度 - 依赖于Realm - `Realm` - Shiro 从 Realm 获取安全数据(如用户、角色、权限),就是说 SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从 Realm 获取相应的用户进行比较以确定用户身份是否合法; - 由于Shiro是不提供用户/授权的,需要我们去自定义Realm <font color='red'>依赖关系</font>: `ShiroFilterFactoryBean`==>`DefaultWebSecurityManager`==>自定义`Realm` ```java //ShiroFilterFactoryBean设置安全管理器defaultWebSecurityManager ShiroFilterFactoryBean factoryBean=new ShiroFilterFactoryBean(); //设置安全管理器 factoryBean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
1 2 3 4 DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); securityManager.setRealm(userRealm);
1 2 3 4 5 @Bean public UserRealm userRealm () return new UserRealm(); }
自定义Realm类 UserRealm
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm @Autowired UserMapper userMapper; @Override protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo (PrincipalCollection principals) System.out.println("执行了授权==》" +principals); SimpleAuthorizationInfo info=new SimpleAuthorizationInfo(); Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); User currentUser = (User)subject.getPrincipal(); info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms()); return info; } @Override protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo (AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException System.out.println("执行了身份认证==》" +token); UsernamePasswordToken token1=(UsernamePasswordToken) token; User user = userMapper.selectUserByName(token1.getUsername()); if (user==null ){ return null ; } return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPwd(),"" ); } }
Controller层的登录请求
Shiro记住我
参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43298012/article/details/87890956?utm_medium=distribute.wap_relevant.none-task-blog-baidujs_baidulandingword-0
记住我功能在各各网站是比较常见的,实现起来也都差不多,主要就是利用cookie来实现,而shiro对记住我功能的实现也是比较简单的,只需要几步即可。
Shiro配置记住我步骤:
在MyShiroConfig中添加以下Bean
记住我cookie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 @Bean public SimpleCookie rememberMeCookie () SimpleCookie simpleCookie=new SimpleCookie("rememberMe" ); simpleCookie.setHttpOnly(true ); simpleCookie.setPath("/" ); simpleCookie.setMaxAge(60 *60 *24 *3 ); return simpleCookie; }
记住我Cookie的安全管理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 @Bean public CookieRememberMeManager rememberMeManager () CookieRememberMeManager rememberMeManager=new CookieRememberMeManager(); rememberMeManager.setCookie(rememberMeCookie()); rememberMeManager.setCipherKey(Base64.getDecoder().decode("4AvVhmFLUs0KTA3Kprsdag==" )); return rememberMeManager; }
记住我的过滤器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Bean public FormAuthenticationFilter formAuthenticationFilter () FormAuthenticationFilter filter=new FormAuthenticationFilter(); filter.setRememberMeParam("rememberMe" ); return filter; }
以上准备完成后,开始和Shiro整合
在核心安全管理器中配置rememberMe的安全管理器
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Bean("SecurityManager") public DefaultWebSecurityManager DefaultWebSecurityManager (@Qualifier("userRealm") UserRealm userRealm) DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager=new DefaultWebSecurityManager(); securityManager.setRealm(userRealm); securityManager.setRememberMeManager(rememberMeManager()); return securityManager; }
**修改shirFilter中拦截请求的规则,将/从authc 改为user
但是注意前往登录和处理登录的请求就不是user了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Bean("shiroFilterFactoryBean") public ShiroFilterFactoryBean ShiroFilterFactoryBean (@Qualifier("SecurityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager) ... Map<String, String> filterMap=new LinkedHashMap<>(); filterMap.put("/add" ,"perms[user:add]" ); filterMap.put("/update" ,"perms[user:update]" ); filterMap.put("/" ,"anon" ); filterMap.put("/login" ,"anon" ); filterMap.put("/**" ,"user" ); .... }
更改HelloController中login方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @RequestMapping("/login") public String login (String username, String password,boolean rememberMe, Model model) System.out.println("用户信息:" +username+":" +password+":" +rememberMe); Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject(); UsernamePasswordToken token=new UsernamePasswordToken(username,password,rememberMe); ... }
登陆页面加入rememberMe功能
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <form th:action ="@{/login}" > <label th:text ="${msg}" style ="color: red" > </label > 用户名: <input type ="text" name ="username" /> 密码: <input type ="password" name ="password" /> <input type ="checkbox" name ="rememberMe" > 记住我 <input type ="submit" value ="登录" > </form >
Shiro和thymeleaf整合
导入整合包
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 <dependency > <groupId > com.github.theborakompanioni</groupId > <artifactId > thymeleaf-extras-shiro</artifactId > <version > 2.0.0</version > </dependency >
配置thymeleaf的Shiro的方言(可以写在Shiro的配置文件中)
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Bean public ShiroDialect shiroDialect () return new ShiroDialect(); }
thymeleaf的命名空间
1 xmlns:shiro="http://www.pollix.at/thymeleaf/shiro"
可以写的一些标签
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 <body > 首页 <div shiro:notAuthenticated ="" > <a th:href ="@{/toLogin}" > 登录</a > </div > <a th:href ="@{/add}" shiro:hasPermission ="user:add" > 添加</a > <a th:href ="@{/update}" shiro:hasPermission ="user:update" > 修改</a > </body >
浏览器中rememberMe的值
其实是将用户信息加密后放到前台的(包含密码),在项目中user对象信息过于庞大,不能全部存入Cookie,Cookie对长度有一定的限制。
15,Swagger
帮助文档:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/275708279 (比较高级)
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44203158/article/details/109137799 (推荐看这个)
1,介绍
Swagger 是一套基于 OpenAPI 规范(OpenAPI Specification,OAS)构建的开源工具,后来成为了 Open API 标准的主要定义者。
swagger2于17年停止维护,现在最新的版本为17年发布的 Swagger3(Open Api3)。
2,springfox介绍
SpringFox是 spring 社区维护的一个项目(非官方)
3,springfox-swagger 2
SpringBoot项目整合swagger2需要用到两个依赖:springfox-swagger2和springfox-swagger-ui,用于自动生成swagger文档。
springfox-swagger2:这个组件的功能用于帮助我们自动生成描述API的json文件
4,SpringFox 3.0.0 发布
Spring5,Webflux支持(仅支持请求映射,尚不支持功能端点)。
Spring Integration支持。
SpringBoot支持springfox Boot starter依赖性(零配置、自动配置支持)。
支持OpenApi 3.0.3。
零依赖。几乎只需要spring-plugin,swagger-core ,现有的swagger2注释将继续工作并丰富openapi3.0规范。
5,使用Swagger3.0
导入依赖:
1 2 3 4 5 <dependency > <groupId > io.springfox</groupId > <artifactId > springfox-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 3.0.0</version > </dependency >
1, application.yml配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 spring: application: name: springfox-swagger server: port: 8080 swagger: enable: true application-name: ${spring.application.name} application-version: 1.0 application-description: springfox swagger 3.0 整合Demo try-host: http://localhost:${server.port}
2, 自定义一个swagger配置类 SwaggerProperties.class
注意注解@ConfigurationProperties的使用
代表被修饰的类可以通过前缀prefix = "XXX",yaml赋值.
同时注解@ConfigurationProperties需要搭配注解@Component托管给ioc容器
帮助文档:https://www.cnblogs.com/jimoer/p/11374229.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 package cn.xpp011.config;import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "swagger") public class SwaggerProperties private Boolean enable; private String applicationName; private String applicationVersion; private String applicationDescription; private String tryHost; public Boolean getEnable () return enable; } public void setEnable (Boolean enable) this .enable = enable; } public String getApplicationName () return applicationName; } public void setApplicationName (String applicationName) this .applicationName = applicationName; } public String getApplicationVersion () return applicationVersion; } public void setApplicationVersion (String applicationVersion) this .applicationVersion = applicationVersion; } public String getApplicationDescription () return applicationDescription; } public void setApplicationDescription (String applicationDescription) this .applicationDescription = applicationDescription; } public String getTryHost () return tryHost; } public void setTryHost (String tryHost) this .tryHost = tryHost; } }
3, springfox swagger3配置类SwaggerConfiguration.class
注解@EnableOpenApi大致意思就是**「只有在配置类标注了@EnableOpenApi这个注解才会生成Swagger文档」**。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 @EnableOpenApi @Configuration public class SwaggerConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer private final SwaggerProperties swaggerProperties; public SwaggerConfiguration (SwaggerProperties swaggerProperties) this .swaggerProperties = swaggerProperties; } @Bean public Docket createRestApi () return new Docket(DocumentationType.OAS_30).pathMapping("/" ) .groupName("lighter" ) .enable(swaggerProperties.getEnable()) .apiInfo(apiInfo("lighter" ,null ,"123456@gmail.com" )) .host(swaggerProperties.getTryHost()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.xpp011.controller" )) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build() .protocols(newHashSet("https" , "http" )) .securitySchemes(securitySchemes()) .securityContexts(securityContexts()); } private ApiInfo apiInfo (String name,String url,String email) return new ApiInfoBuilder().title(swaggerProperties.getApplicationName() + " Api Doc" ) .description(swaggerProperties.getApplicationDescription()) .contact(new Contact(name, url,email )) .version("Application Version: " + swaggerProperties.getApplicationVersion() + ", Spring Boot Version: " + SpringBootVersion.getVersion()) .build(); } private List<SecurityScheme> securitySchemes () ApiKey apiKey = new ApiKey("BASE_TOKEN" , "token" , In.HEADER.toValue()); return Collections.singletonList(apiKey); } private List<SecurityContext> securityContexts () return Collections.singletonList( SecurityContext.builder() .securityReferences(Collections.singletonList(new SecurityReference("BASE_TOKEN" , new AuthorizationScope[]{new AuthorizationScope("global" , "" )}))) .build() ); } @SafeVarargs private final <T> Set<T> newHashSet (T... ts) { if (ts.length > 0 ) { return new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(ts)); } return null ; } @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") @Override public void addInterceptors (InterceptorRegistry registry) try { Field registrationsField = FieldUtils.getField(InterceptorRegistry.class, "registrations" , true ); List<InterceptorRegistration> registrations = (List<InterceptorRegistration>) ReflectionUtils.getField(registrationsField, registry); if (registrations != null ) { for (InterceptorRegistration interceptorRegistration : registrations) { interceptorRegistration .excludePathPatterns("/swagger**/**" ) .excludePathPatterns("/webjars/**" ) .excludePathPatterns("/v3/**" ) .excludePathPatterns("/doc.html" ); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
配置完成后可访问:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html 查看
6,Swagger分组
其实在Swagger中分组就是对应着不同的Docket
我们只需要想IOC容器中注册不同的Docket即可
这里组被分成了两个,分别是root,lighter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 @Bean public Docket rootRestApi () return new Docket(DocumentationType.OAS_30).pathMapping("/" ) .groupName("root" ) .enable(swaggerProperties.getEnable()) .apiInfo(apiInfo("root" ,"https://xpp011.xn" ,"2500176776@qq.com" )) .host(swaggerProperties.getTryHost()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.any()) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build() .protocols(newHashSet("https" , "http" )) .securitySchemes(securitySchemes()) .securityContexts(securityContexts()); } @Bean public Docket createRestApi () return new Docket(DocumentationType.OAS_30).pathMapping("/" ) .groupName("lighter" ) .enable(swaggerProperties.getEnable()) .apiInfo(apiInfo("lighter" ,null ,"123456@gmail.com" )) .host(swaggerProperties.getTryHost()) .select() .apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("cn.xpp011.controller" )) .paths(PathSelectors.any()) .build() .protocols(newHashSet("https" , "http" )) .securitySchemes(securitySchemes()) .securityContexts(securityContexts()); }
7,测试注解
帮助文档:http://c.biancheng.net/view/5533.html
@Api
@Api 用在类上,说明该类的作用。
1 2 3 @Api(tags = "用户登录控制类") @Controller public class HelloController
ApiOperation
@ApiOperation 用在 Controller 里的方法上,说明方法的作用,每一个接口的定义。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Controller public class HelloController @ApiOperation("首页请求") @RequestMapping({"/","/index"}) public String index () return "index" ; } }
ApiParam
@ApiParam 用于 Controller 中方法的参数说明。
1 2 3 @ApiOperation("处理登录请求") @RequestMapping("/login") public String login (@ApiParam("用户名字") String username,@ApiParam("用户密码") String password,@ApiParam("是否勾选记得我") boolean rememberMe, Model model)
@ApiModel
@ApiModel 用在实体类上
1 2 @ApiModel(value = "用户类",discriminator = "实体类") public class User implements Serializable
ApiModelProperty
@ApiModelProperty() 用于实体类的字段
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @ApiModelProperty("用户id") private int id;@ApiModelProperty("用户名字") private String name;@ApiModelProperty("用户密码") private String pwd;@ApiModelProperty("用户权限") private String perms;
16,异步任务
异步任务主要帮助用户提升体验,比如发送邮件,后台发送邮件是比较慢的过程,需要联网等等,而用户就会需要等待多时,而我们开启异步任务时,将邮件发送变成一个多线程任务,让用户先做其他事情,就会大大增加用户体验
如何开启异步任务
在需要异步的类上加上一个注解@Async声明这是一个异步任务,那样程序调用该类时就会开启异步
该注解可以加在类上或者方法上
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Async @Service public class AsyncTest public void test () try { Thread.sleep(3000 ); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("hello" ); } }
在SpringBoot主启动类上加上@EnableAsync注解,启动异步
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @EnableAsync @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootAsyncApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAsyncApplication.class, args); } }
17,文件上传,邮件发送
邮件发送
参考文档:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_43647359/article/details/104638599
首先导入依赖
由于我发现springBoot启动器mail的依赖包中,javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage是缺失的,所有还需要额外导入javax.mail的mail依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-mail</artifactId > <version > 2.4.5</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > javax.mail</groupId > <artifactId > mail</artifactId > <version > 1.4.7</version > </dependency >
yaml配置文件中配置发送邮件需要的信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 spring: mail: host: smtp.qq.com default-encoding: utf-8 username: 2500176776 @qq.com password: ddkrojojfylldhic properties: mail: smtp: socketFactoryClass: javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory
一个简单的邮件
项目中要把它提成一个方法,这里先偷懒
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 public String SimpleMailSend () String msg="邮件发送成功" ; try { SimpleMailMessage message=new SimpleMailMessage(); message.setSubject("主题" ); message.setText("邮件内容" ); message.setTo("2500176776@qq.com" ); message.setFrom("2500176776@qq.com" ); javaMailSender.send(message); return msg; }catch (Exception e){ msg="邮件发送失败" ; return msg; } }
一个复杂邮件
项目中要把它提成一个方法,这里先偷懒
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 public String MimeMailSend () String msg="邮件发送成功" ; try { MimeMessage mimeMessage = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage(); MimeMessageHelper helper=new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,true ); helper.setSubject("附件邮件主题" ); helper.setText("<h1>你好</h1>" ,true ); helper.setTo("2500176776@qq.com" ); helper.setFrom("2500176776@qq.com" ); helper.addAttachment("1.png" ,new File("D:\\win10桌面存放\\java\\赫夫曼思想.png" )); javaMailSender.send(mimeMessage); return msg; }catch (Exception e){ msg="邮件发送失败" ; return msg; } }
将图片插入在邮件中
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public void sendImgResMail () throws MessagingException MimeMessage mimeMessage = javaMailSender.createMimeMessage(); MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,true ); helper.setSubject("这是一封测试邮件" ); helper.setFrom("bai211425401@qq.com" ); helper.setTo("1712900841@qq.com" ); helper.setSentDate(new Date()); helper.setText("<p>hello 大家好,我是一封测试邮件,我包含了两张图片,分别如下</p><p>第一张图片:</p><img src='cid:p01'/><p>第二张图片:</p><img src='cid:p02'/>" ,true ); helper.addInline("p01" ,new FileSystemResource(new File("C:\\Users\\bai\\Pictures\\Camera Roll\\img\\1.png" ))); helper.addInline("p02" ,new FileSystemResource(new File("C:\\Users\\bai\\Pictures\\Camera Roll\\img\\2.png" ))); javaMailSender.send(mimeMessage); }
注意:
在实际开发中,我们不可能让用户等待邮件发送完毕,所以我们要将邮件发送变成一个异步任务
在邮件发送的类上加入注解@Async声明是一个异步任务
1 2 @Async public class MailSend
在SpringBoot主启动类中加入注解@EnableAsync开启异步任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @EnableAsync @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootAsyncApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAsyncApplication.class, args); } }
文件上传
前端
1 2 3 4 <form action ="/fileUpload" method ="post" enctype ="multipart/form-data" > <input type ="file" name ="file" > <input type ="submit" value ="上传" > </form >
后端接口
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @PostMapping("/fileUpload") @ResponseBody public String fileUpload (MultipartFile file, HttpServletRequest request) String format = sdf.format(new Date()); String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/img/" ) + format; System.out.println("文件保存路径:" + path); File realPath = new File(path); if (!realPath.exists()) { realPath.mkdirs(); } String oldName = file.getOriginalFilename(); String newName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + oldName.substring(oldName.lastIndexOf("." )); try { file.transferTo(new File(realPath, newName)); String overPath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + "/img/" + format + newName; return overPath; } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return "error" ; }
ajax请求
axaj请求后端接口基本不用变
前端(记住需要导入jquery)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 <div id ="msg" > </div > <input type ="file" id ="file" > <input type ="button" onclick ="UpLoad()" value ="提交" > <script > function UpLoad ( var file=$("#file" )[0 ].files[0 ]; var formDate=new FormData(); formDate.append("file" ,file); console .log("开始" ); $.ajax({ type :"post" , url :"/fileUpload" , processData : false , contentType : false , data :formDate, success :function (msg ) $("#msg" ).html(msg); } } ) } </script >
多文件上传
前端
前端只需要设置 input标案加入属性 multiple 实现多文件上传
1 2 3 4 5 <form action ="/fileUploads" method ="post" enctype ="multipart/form-data" > <input type ="file" name ="files" multiple > <input type ="submit" value ="上传" > </form >
后端
后端大致一样
接收的MultipartFile改为数组形式 存储多个文件
最后遍历该数组并保存
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 @PostMapping("/fileUploads") @ResponseBody public String fileUploads (MultipartFile[] files, HttpServletRequest request) String format = sdf.format(new Date()); String path = request.getServletContext().getRealPath("/img/" ) + format; System.out.println("文件保存路径:" + path); File realPath = new File(path); if (!realPath.exists()) { realPath.mkdirs(); } for (MultipartFile file : files) { String oldName = file.getOriginalFilename(); String newName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + oldName.substring(oldName.lastIndexOf("." )); try { file.transferTo(new File(realPath, newName)); String overPath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + "/img/" + format + newName; System.out.println(overPath); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } return "success" ; }
18,定时任务
注解 @EnableScheduling
开启定时任务,在主启动类上加
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 @EnableScheduling @SpringBootApplication public class SpringbootAsyncApplication public static void main (String[] args) SpringApplication.run(SpringbootAsyncApplication.class, args); } }
注解 @scheduled
通过cron表达式进行定时,作用域在方法上,不要加在类上
星期天到星期六的每月每日每时每分每秒执行hello方法
1 2 3 4 @org .springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled(cron = "* * * * * 0-6 " )public void hello () System.out.println("hello" ); }
cron表达式
常用表达式例子
(1)0 0 2 1 * ? * 表示在每月的1日的凌晨2点调整任务
(2)0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 表示周一到周五每天上午10:15执行作业
(3)0 15 10 ? 6L 2002-2006 表示2002-2006年的每个月的最后一个星期五上午10:15执行作
(4)0 0 10,14,16 * * ? 每天上午10点,下午2点,4点
(5)0 0/30 9-17 * * ? 朝九晚五工作时间内每半小时
(6)0 0 12 ? * WED 表示每个星期三中午12点
(7)0 0 12 * * ? 每天中午12点触发
(8)0 15 10 ? * * 每天上午10:15触发
(9)0 15 10 * * ? 每天上午10:15触发
(10)0 15 10 * * ? * 每天上午10:15触发
(11)0 15 10 * * ? 2005 2005年的每天上午10:15触发
(12)0 * 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:59期间的每1分钟触发
(13)0 0/5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:55期间的每5分钟触发
(14)0 0/5 14,18 * * ? 在每天下午2点到2:55期间和下午6点到6:55期间的每5分钟触发
(15)0 0-5 14 * * ? 在每天下午2点到下午2:05期间的每1分钟触发
(16)0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED 每年三月的星期三的下午2:10和2:44触发
(17)0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI 周一至周五的上午10:15触发
(18)0 15 10 15 * ? 每月15日上午10:15触发
(19)0 15 10 L * ? 每月最后一日的上午10:15触发
(20)0 15 10 ? * 6L 每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
(21)0 15 10 ? * 6L 2002-2005 2002年至2005年的每月的最后一个星期五上午10:15触发
(22)0 15 10 ? * 6#3 每月的第三个星期五上午10:15触发
学习网址:https://www.cnblogs.com/javahr/p/8318728.html
在线转换器网址:https://qqe2.com/cron 也可以将cron表达式转为看得懂的文字
19,Dubbo
Dubbo(读音[ˈdʌbəʊ])是阿里巴巴公司开源的一个高性能优秀的服务框架 ,使得应用可通过高性能的 RPC 实现服务的输出和输入功能,可以和 [1] Spring 框架无缝集成。
Dubbo是一款高性能、轻量级的开源Java RPC框架,它提供了三大核心能力:面向接口的远程方法调用,智能容错和负载均衡,以及服务自动注册和发现。
架构
Dubbo 架构
节点角色说明
节点
角色说明
Provider暴露服务的服务提供方
Consumer调用远程服务的服务消费方
Registry服务注册与发现的注册中心
Monitor统计服务的调用次数和调用时间的监控中心
Container服务运行容器
调用关系说明
服务容器负责启动,加载,运行服务提供者。
服务提供者在启动时,向注册中心注册自己提供的服务。
服务消费者在启动时,向注册中心订阅自己所需的服务。
注册中心返回服务提供者地址列表给消费者,如果有变更,注册中心将基于长连接推送变更数据给消费者。
服务消费者,从提供者地址列表中,基于软负载均衡算法,选一台提供者进行调用,如果调用失败,再选另一台调用。
服务消费者和提供者,在内存中累计调用次数和调用时间,定时每分钟发送一次统计数据到监控中心。
实现Dubbo和zookeeper
zookeeper
前往zookeeper官网下载:https://zookeeper.apache.org/releases.html 3.6.3为稳定版
下载完成后解压,并运行/bin目录下的zkServer.cmd文件启动zookeeper
dubbo-admin
前往下载dubbo在GetHub上托管的dubbo-admin
dubbo-admin是是一个可视化管理dubbo和zookeeper注册中心的网页
网址:https://github.com/apache/dubbo-admin/tree/master 建议下载master分支的debbo,最新版是vue分离的比较折腾
在项目dubbo-admin-master下,运行cmd,执行mvn clean package -Dmaven.test.skip=true将项目打成jar包
在子项目dubbo-admin的target目录运行打包好的jar包
构建项目
在IDEA中构建两个项目,分别是提供者Provider和消费者Consumer
配置端口,避免端口冲突
server.port=XXXX
分别在两个项目中导入依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 <dependency > <groupId > com.github.mxsm</groupId > <artifactId > zkclient-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 1.0.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.dubbo</groupId > <artifactId > dubbo-spring-boot-starter</artifactId > <version > 2.7.11</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.curator</groupId > <artifactId > curator-framework</artifactId > <version > 5.1.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.curator</groupId > <artifactId > curator-recipes</artifactId > <version > 5.1.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.zookeeper</groupId > <artifactId > zookeeper</artifactId > <version > 3.7.0</version > <exclusions > <exclusion > <groupId > org.slf4j</groupId > <artifactId > slf4j-log4j12</artifactId > </exclusion > </exclusions > </dependency >
springboot-provider
编写配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 server.port =8081 dubbo.application.name =provider-server dubbo.registry.address =zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181 dubbo.scan.base-packages =cn.xpp011.service
在提供者springboot-provider项目中书写想要暴露的服务
注意TicketServiceImpl类实现接口TicketService,接口TicketService中就一个方法ticket
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 package cn.xpp011.service;@DubboService @Service public class TicketServiceImpl implements TicketService @Override public String ticket () return "《成都-->上海》" ; } }
在主启动类中加入注解@EnableDubbo启动Dubbo
1 2 3 @SpringBootApplication @EnableDubbo public class SpringbootProviderApplication
springboot-consumer
编写配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 server.port =8082 dubbo.application.name =consumer-server dubbo.registry.address =zookeeper://127.0.0.1:2181
在消费者类中编写服务类,同时调用提供者springboot-provider 项目中暴露的服务类
注意如果想要拿到别的项目暴露的服务类,需要编写该服务类实现的接口,包路径也必须相同
拿到其他项目暴露服务类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Service public class ConsumerTicket @DubboReference TicketService ticketService; public void consumer () String ticket = ticketService.ticket(); System.out.println("购买了:" +ticket); } }
运行消费者springboot-consumer
最后可以在dubbo-admin的网页地址http://localhost:7001
可视化的看到暴露的服务类
思考
1,为什么dubbo-admin可以可视化的看到提供者暴露的服务类呢
在dubbo-admin-master的配置文件中我们看到了,它已经配置了zookeeper注册中心的地址。所以dubbo-admin拿到了注册中心的数据。
所以我们zookeeper注册中心的端口修改时,我们的dubbo-admin-master的配置文件也要修改哦;
2,那zookeeper注册中心是怎么拿到提供者暴露的服务类的呢
其实在提供者springboot-provider 项目中配置了注册中心的地址
并提供服务类的注解@DubboService将该服务类在注册中心注册
3,那消费者是怎么拿到暴露的服务的呢
这就比较简单了
消费者springboot-consumer 项目也配置了zookeeper注册中心的地址
并通过注解@DubboReference从注册中心拿取相应类型,相应包路径的服务类
20,跨域请求(cors)
1.什么是跨域?
跨域:指的是浏览器不能执行其他网站的脚本。它是由浏览器的同源策略造成的,是浏览器对javascript施加的安全限制。
例如:a页面想获取b页面资源,如果a、b页面的协议、域名、端口、子域名不同,所进行的访问行动都是跨域的,而浏览器为了安全问题一般都限制了跨域访问,也就是不允许跨域请求资源。注意:跨域限制访问,其实是浏览器的限制 。理解这一点很重要!!!
同源策略:是指协议,域名,端口都要相同,其中有一个不同都会产生跨域;
那SpringBoot如何解决跨域请求呢
注解
在SpringBoot中解决跨域请求是相当简单的
只需要注解@CrossOrigin(“域名地址:端口”)
当我们加上该注解的使用那么该方法或者类下的所有方法 都会被指定 域名:端口允许方法
实现Cors 跨域资源共享
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @RestController public class HelloController @GetMapping("/hello") public String gethello () return "hello cors:get" ; } @PutMapping("/hello") public String puthello () return "hello cors:put" ; } }
配置类
但是在项目很大的使用,加注解的方式就显得不是很明智了,那么通过Java配置类的方式解救跨域请求
实现WebMvcConfigurer接口,并实现跨域资源共享映射方法addCorsMappings方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Configuration public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer @Override public void addCorsMappings (CorsRegistry registry) registry.addMapping("/**" ) .allowedOrigins("http://localhost:8082" ) .allowedHeaders("*" ) .allowedMethods("*" ) .maxAge(3 * 1000 ); } }
关于探测请求
在put请求方式中,它第一次会发送两次请求
第一次是探测请求,判断服务器是否支持该请求地址,如果支持那么就会发送第二次正式请求
那探测请求其实不用每次都发,我们可以设置一个探测请求有效期,在该有效期内就不用每次都发探测请求了,也就是配置类的maxAge()方法
21,系统启动任务
CommandLineRunner 系统启动任务,可以在系统启动之前做一些事情,比如初始化参数等等
自定义Java配置类 实现启动命令接口CommandLineRunner
实现run方法在其中可以做一些系统启动任务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @Configuration @Order(100) public class MyComm implements CommandLineRunner @Override public void run (String... args) throws Exception System.out.println("系统启动任务1,参数:" + Arrays.toString(args)); } }
注意注解@Order当我们有多个系统启动任务类时,设置优先级就很必要
系统启动任务的优先级 默认为2的31次方减一 数字越小优先级越高
ApplicationRunner
ApplicationRunner也是一个系统启动类,只不过它可以获取kv键值对形式的参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Configuration @Order(99) public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner @Override public void run (ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception String[] sourceArgs = args.getSourceArgs(); System.out.println("sourceArgs : " + Arrays.toString(sourceArgs)); List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs(); nonOptionArgs.forEach((v)->{ System.out.println("v : " +v); }); Set<String> optionNames = args.getOptionNames(); optionNames.forEach((k)->{ System.out.println(k+" : " +args.getOptionValues(k)); }); } }
执行效果
22,SpringBoot—Aop
前置
JoinPoint 对象
JoinPoint 对象****封装了SpringAop中切面方法的信息*,在切面方法中添加 ,就可以获取到封装了该方法信息的 常用api:
方法名
功能
Signature getSignature();
获取封装了署名信息的对象,在该对象中可以获取到目标方法名,所属类的Class等信息
Object[] getArgs();
获取传入目标方法的参数对象
Object getTarget();
获取被代理的对象
Object getThis();
获取代理对象
ProceedingJoinPoint对象
*ProceedingJoinPoint对象是JoinPoint的子接口,该对象只用在@Around的切面方法中,* Object proceed() throws Throwable //执行目标方法Object proceed(Object[] var1) throws Throwable //传入的新的参数去执行目标方法
导入aop依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId > </dependency >
自定义切面类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 package cn.xpp011.Config;import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component @Aspect public class MyAspect @Pointcut("execution(* cn.xpp011.Service.*.*(..))") public void pc1 () @Before("pc1()") public void before (JoinPoint jp) String name = jp.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println(name+"方法执行前" ); } @After("pc1()") public void After (JoinPoint jp) String name = jp.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println(name+"方法执行后" ); } @AfterReturning(value = "pc1()",returning = "o") public Object AfterReturning (JoinPoint jp,Object o) String name = jp.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println(name+"方法的返回值:" +o); return o; } @AfterThrowing(value = "pc1()",throwing = "e") public void AfterThrowing (JoinPoint jp,Exception e) String name = jp.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println(name+"方法报出的异常:" +e.getMessage()); } @Around("pc1()") public Object a (ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable System.out.println("环绕通知" ); Object proceed = pjp.proceed(); return proceed; } }
23,整合Redis
Linux安装redis
1.首先下载 Redis,下载地址https://redis.io/,下载获得 redis-4.0.8.tar.gz 后将它放入我们的 Linux 目录 /opt
2./opt 目录下,对文件进行解压,解压命令: tar -zxvf redis-4.0.8.tar.gz ,如下:
3.解压完成后出现文件夹:redis-4.0.8,进入到该目录中: cd redis-4.0.8
4.在 redis-4.0.8 目录下执行 make 命令进行编译
5.如果 make 完成后继续执行 make install 进行安装
OK,至此,我们的 redis 就算安装成功了。
6.在我们启动之前,需要先做一个简单的配置:修改 redis.conf 文件,将里面的 daemonize no 改成 yes,让服务在后台启动,如下:
7.启动,通过redis-server redis.conf命令启动redis,如下:
8.测试
首先我们可以通过 redis-cli 命令进入到控制台,然后通过 ping 命令进行连通性测试,如果看到 pong ,表示连接成功了,如下:
9.关闭,通过 shutdown 命令我们可以关闭实例,如下:
远程连接
1,修改redis服务器的配置文件vim redis.conf
2,注释以下绑定的主机地址
#bind 127.0.0.1
3,关闭保护模式
组合拳
4,开启端口6379 firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=6379/tcp --permanent
5,重启防火墙 firewall-cmd --reload
6,重启redis
整合redis
加入依赖
redis必须和security一起使用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId > </dependency >
配置文件
业务类
24,Linux安装Nginx
首先下载 Nginx(可去官网nginx.org获取最新下载地址)
1 wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.17.0.tar.gz
然后解压下载的目录,进入解压目录中,在编译安装之前,需要安装两个依赖:(如果没有安装C++编译环境则需要先安装C++编译环境)
1 2 yum -y install pcre-devel yum -y install openssl openssl-devel
然后开始编译安装:
1 2 3 ./configure make make install
装好之后,默认安装位置在 :
1 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
进入到该目录的 sbin 目录下,执行 nginx 即可启动 Nginx :
Nginx 启动成功之后,在浏览器中直接访问 Nginx 地址:
看到如上页面,表示 Nginx 已经安装成功了。
如果修改了 Nginx 配置,则可以通过如下命令重新加载 Nginx 配置文件:
25,Session共享
Session共享的前提是有两个及以上的服务器,这里就涉及到分布式等操作
在我们创建项目时,记住需要勾选Spring Session依赖,这样SpringBoot就可以帮助我们自动配置一些Session配置
我们启动两个tomcat,这两个tomcat配置了同一个redis
此时我们访问这两个项目就会得到相同的session
我们查看redis,发现他已经存放了相关的session信息
使用Nginx进行负载均衡
将jar包上传至linux,启动两个tomcat,判断tomcat是否可以正常访问
配置Nginx,实现负载均衡,
加入Nginx的默认路径
修改配置文件Nginx.config
解释:
在这段配置中:
upstream 表示配置上游服务器
javaboy.org 表示服务器集群的名字,这个可以随意取名字upstream 里边配置的是一个个的单独服务
weight 表示服务的权重,意味者将有多少比例的请求从 Nginx 上转发到该服务上
location 中的 proxy_pass 表示请求转发的地址,/ 表示拦截到所有的请求,转发转发到刚刚配置好的服务集群中
proxy_redirect 表示设置当发生重定向请求时,nginx 自动修正响应头数据(默认是 Tomcat 返回重定向,此时重定向的地址是 Tomcat 的地址,我们需要将之修改使之成为 Nginx 的地址)。
配置完成后,将本地的 Spring Boot 打包好的 jar 上传到 Linux ,然后在 Linux 上分别启动两个 Spring Boot 实例:
1 2 nohup java -jar sessionshare-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8080 & nohup java -jar sessionshare-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar --server.port=8081 &
其中
nohup 表示当终端关闭时,Spring Boot 不要停止运行
& 表示让 Spring Boot 在后台启动
配置完成后,重启 Nginx:
1 /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
Nginx 启动成功后,我们首先手动清除 Redis 上的数据,然后访问 192.168.66.128/set 表示向 session 中保存数据,这个请求首先会到达 Nginx 上,再由 Nginx 转发给某一个 Spring Boot 实例:
如上,表示端口为 8081 的 Spring Boot 处理了这个 /set 请求,再访问 /get 请求:
可以看到,/get 请求是被端口为 8080 的服务所处理的。
26,SpringBoot集成RabbitMQ
简介
RabbitMQ 是一个由 Erlang 语言开发的 AMQP 的开源实现。
AMQP :Advanced Message Queue,高级消息队列协议。它是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计,基于此协议的客户端与消息中间件可传递消息,并不受产品、开发语言等条件的限制。
RabbitMQ 最初起源于金融系统,用于在分布式系统中存储转发消息,在易用性、扩展性、高可用性等方面表现不俗。具体特点包括:
可靠性(Reliability)
灵活的路由(Flexible Routing)
消息集群(Clustering)
高可用(Highly Available Queues)
多种协议(Multi-protocol)
多语言客户端(Many Clients)
管理界面(Management UI)
跟踪机制(Tracing)
插件机制(Plugin System)
安装和使用 首先在Linux中使用docker安装RabbitMQ ——执行以下命令
docker run -d --hostname my-rabbit --name some-rabbit -p 15672:15672 -p 5672:5672 rabbitmq:3-management
说明:
-p 端口映射
–name 容器实例名称
-d 后台运行
5672 客户端与rabbitmq通信端口
15672 rabbitmq web管理端口 访问http://ip:15672 默认用户:guest 默认密码:guest
docker查看运行状态
docker ps
端口说明
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 4369 -- erlang发现口 5672 --client端通信口 15672 -- 管理界面ui端口 25672 -- server间内部通信口
在防火墙中开放指定端口
开启指定端口
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=15672/tcp --permanent
重启防火墙
firewall-cmd --reload
交换机模式
常用的交换机有以下三种,因为消费者是从队列获取信息的,队列是绑定交换机的(一般),所以对应的消息推送/接收模式也会有以下几种:
Direct Exchange
直连型交换机,根据消息携带的路由键将消息投递给对应队列。
大致流程,有一个队列绑定到一个直连交换机上,同时赋予一个路由键 routing key 。
Fanout Exchange
扇型交换机,这个交换机没有路由键概念,就算你绑了路由键也是无视的。 这个交换机在接收到消息后,会直接转发到绑定到它上面的所有队列。
Topic Exchange
主题交换机,这个交换机其实跟直连交换机流程差不多,但是它的特点就是在它的路由键和绑定键之间是有规则的。
(井号) 用来表示任意数量 (零个或多个)单词
通配的绑定键是跟队列进行绑定的,举个小例子.TT. 队列Q2绑定键为 TT.#如果一条消息携带的路由键为TT.AA.BB ,那么队列Q2将会收到;
主题交换机是非常强大的,为啥这么膨胀?
另外还有 Header Exchange 头交换机 ,Default Exchange 默认交换机,Dead Letter Exchange 死信交换机,这几个该篇暂不做讲述。
SpringBoot配置信息
1 2 3 4 spring.rabbitmq.host=192.168 .32 .131 spring.rabbitmq.username=xpp011 spring.rabbitmq.password=xpp011 spring.rabbitmq.port=5672
代码实现
直连交换机模式(Direct Exchange) RabbitDirectConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Configuration public class RabbitDirectConfig private static final String DIRECTNAME="directExchange" ; @Bean public Queue queue () return new Queue("directQueue" ); } @Bean DirectExchange directExchange () { return new DirectExchange(DIRECTNAME,true ,false ); } @Bean Binding binding () { return BindingBuilder.bind(queue()).to(directExchange()).with("direct" ); } }
消费者
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 @Component public class DirectReceiver @RabbitListener( queues = "directQueue") public void handler1 (String msg) System.out.println("handler1 -> " + msg); } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 @Test void contextLoads () rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("directExchange" ,"direct" ,"你好 rabbit消息队列" ); }
扇形交换机(Fanout Exchange) RabbitFanoutConfig配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 @Configuration public class RabbitFanoutConfig public static final String FANOUTNAME="fanoutExchange" ; @Bean public Queue queueOne () return new Queue("fanoutQueueOne" ); } @Bean public Queue queueTwo () return new Queue("fanoutQueueTwo" ); } @Bean FanoutExchange fanoutExchange () { return new FanoutExchange(FANOUTNAME,true ,false ); } @Bean Binding bindingOne () { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueOne()).to(fanoutExchange()); } @Bean Binding bindingTwo () { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueTwo()).to(fanoutExchange()); } }
监听类FanoutReceiver
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @Component public class FanoutReceiver @RabbitListener(queues = "fanoutQueueOne") public void ListenerOne (String msg) System.out.println("ListenerOne -> " + msg); } @RabbitListener(queues = "fanoutQueueTwo") public void ListenerTwo (String msg) System.out.println("ListenerTwo -> " + msg); } }
测试
1 2 3 4 5 @Test void FanoutTest () rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitFanoutConfig.FANOUTNAME,null ,"你好 扇形交换机转发" ); }
主题交换机(Topic Exchange) * (星号) 用来表示一个单词 (必须出现的) (井号) 用来表示任意数量(零个或多个)单词
同时我们在写入toutingKey时,通配符连接点必须加. 不然无法识别通配符
RabbitTopicConfig配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 @Configuration public class RabbitTopicConfig public static final String TOPICNAME="topicExchange" ; @Bean public Queue queueXiaoMi () return new Queue("XiaoMiQueue" ); } @Bean public Queue queueSanXin () return new Queue("SanXinQueue" ); } @Bean public Queue queueHuaVei () return new Queue("HuaWeiQueue" ); } @Bean public Queue Topicqueue () return new Queue("TopicQueue" ); } @Bean TopicExchange topicExchange () { return new TopicExchange(TOPICNAME,true ,false ); } @Bean Binding Topicbinding () { return BindingBuilder.bind(Topicqueue()).to(topicExchange()).with("Topic#" ); } @Bean Binding XiaoMibinding () { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueXiaoMi()).to(topicExchange()).with("#.XiaoMi" ); } @Bean Binding SanXinbinding () { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueSanXin()).to(topicExchange()).with("#.SanXin" ); } @Bean Binding HuaVeibinding () { return BindingBuilder.bind(queueHuaVei()).to(topicExchange()).with("#.HuaWei" ); } }
监听类TopicReceiver
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 @Component public class TopicReceiver @RabbitListener(queues = "XiaoMiQueue") public void XiaoMi (String msg) System.out.println("XiaoMi -> " + msg); } @RabbitListener(queues = "SanXinQueue") public void SanXin (String msg) System.out.println("SanXin -> " + msg); } @RabbitListener(queues = "HuaWeiQueue") public void HuaWei (String msg) System.out.println("HuaWei -> " + msg); } @RabbitListener(queues = "TopicQueue") public void queue (String msg) System.out.println("queue -> " + msg); } }
测试类
当我们写入toutingKey时 它会去寻找符合匹配的toutingKey,并发送到绑定的路由上
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Test void TopicTest () rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitTopicConfig.TOPICNAME,"Topic.XiaoMi" ,"你好小米" ); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitTopicConfig.TOPICNAME,"Topic.HuaWei" ,"你好华为" ); rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(RabbitTopicConfig.TOPICNAME,"Topic.SanXin" ,"你好三星" ); }
SpringSecurity
configure(HttpSecurity http)方法设置登录成功处理器和登录失败处理器,返回JSON数据
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/admin/**" ).hasRole("admin" ) .antMatchers("/user/**" ).hasAnyRole("admin" ,"user" ) .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin() .loginProcessingUrl("/doLogin" ) .loginPage("/login" ) .usernameParameter("username" ) .passwordParameter("password" ) .successHandler(new AuthenticationSuccessHandler() { @Override public void onAuthenticationSuccess (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, Authentication authentication) throws IOException, ServletException resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8" ); Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("status" ,200 ); map.put("msg" ,authentication.getPrincipal()); PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter(); out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map)); out.flush(); out.close(); } }) .failureHandler(new AuthenticationFailureHandler() { @Override public void onAuthenticationFailure (HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp, AuthenticationException e) throws IOException, ServletException resp.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8" ); Map<String,Object> map=new HashMap<>(); map.put("status" ,401 ); if (e instanceof LockedException){ map.put("msg" ,"账户被锁住,登录失败" ); }else if (e instanceof BadCredentialsException){ map.put("msg" ,"用户名或者密码错误,登录失败" ); }else if (e instanceof DisabledException){ map.put("msg" ,"账户被锁定,登录失败" ); }else { map.put("msg" ,"登录失败" ); } PrintWriter out = resp.getWriter(); out.write(new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(map)); out.flush(); out.close(); } }) .permitAll() .and() .csrf().disable(); }
角色继承
该方法直接写在Security的配置类中即可
意思为角色为admin的可以干角色user的事
角色user的可以干visitor的事
注意两个关系之间需要以\n风格,可以看一眼源码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 @Bean public RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy () RoleHierarchyImpl roleHierarchy=new RoleHierarchyImpl(); String role="ROLE_admin > ROLE_user \n ROLE_user > ROLE_visitor" ; roleHierarchy.setHierarchy(role); return roleHierarchy; }
Security动态权限管理
关键类
AntPathMatcher --Spring自带的路径匹配类FilterInvocation --调用过滤器类,可获得请求地址Authentication --包含用户登录信息UserDetails --用户的详细说明接口,创建用户实体类时继承该接口UserDetailsService --用户的服务层接口WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter --自定义Security配置类需要继承的类FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource --自定义过滤器类实现的接口(匹配当前路径的权限)AccessDecisionManager --访问决策管理器(做出最终的访问控制(授权)决定。)
AuthenticationException子类异常详解
这个异常是在登录的时候出现错误时抛出的异常,比如账户锁定,证书失效等,先来看下AuthenticationException常用的的子类:
UsernameNotFoundException 用户找不到
BadCredentialsException 坏的凭据
AccountStatusException 用户状态异常它包含如下子类
AccountExpiredException 账户过期
LockedException账户锁定
DisabledException 账户不可用
CredentialsExpiredException 证书过期
User
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class User implements UserDetails private Integer id; private String username; private String password; private Boolean enabled; private Boolean locked; private List<Role> roles; @Override public Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities() { List<SimpleGrantedAuthority> list=new ArrayList<>(); for (Role role : roles) { list.add(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(role.getName())); } return list; } @Override public boolean isAccountNonExpired () return true ; } @Override public boolean isAccountNonLocked () return !locked; } @Override public boolean isCredentialsNonExpired () return true ; } @Override public boolean isEnabled () return enabled; } }
UserService
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Service public class UserService implements UserDetailsService @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper; @Override public UserDetails loadUserByUsername (String username) throws UsernameNotFoundException User user=userMapper.loadUserByUsername(username); if (user==null ) throw new UsernameNotFoundException("用户不存在" ); user.setRoles(userMapper.getRoleById(user.getId())); return user; } }
MyFilert
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 @Component public class MyFilter implements FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSource @Autowired MenuMapper menuMapper; static AntPathMatcher antPathMatcher=new AntPathMatcher(); @Override public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAttributes (Object object) throws IllegalArgumentException FilterInvocation invocation=(FilterInvocation) object; String requestUrl=invocation.getRequestUrl(); System.out.println("当前请求地址 : " +requestUrl); List<Menu> menuAll = menuMapper.getMenuAll(); for (Menu menu : menuAll) { if (antPathMatcher.match(menu.getPattern(),requestUrl)){ List<Role> roles = menu.getRoles(); String [] res=new String[roles.size()]; for (int i = 0 ; i < roles.size(); i++) { res[i]=roles.get(i).getName(); } return SecurityConfig.createList(res); } } return SecurityConfig.createList("ROLE_login" ); } @Override public Collection<ConfigAttribute> getAllConfigAttributes () return null ; } @Override public boolean supports (Class<?> clazz) return true ; } }
MyAccessDecisionManager
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 @Component public class MyAccessDecisionManager implements AccessDecisionManager @Override public void decide (Authentication authentication, Object object, Collection<ConfigAttribute> configAttributes) throws AccessDeniedException, InsufficientAuthenticationException Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities = authentication.getAuthorities(); for (ConfigAttribute configAttribute : configAttributes) { if ("ROLE_login" .equals(configAttribute.getAttribute())){ if (authentication instanceof AnonymousAuthenticationToken){ throw new AccessDeniedException("非法请求" ); }else { return ; } } for (GrantedAuthority authority : authorities) { if (configAttribute.getAttribute().equals(authority.getAuthority())){ return ; } } } throw new AccessDeniedException("非法请求" ); } @Override public boolean supports (ConfigAttribute attribute) return true ; } @Override public boolean supports (Class<?> clazz) return true ; } }
SecurityConfig
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Autowired UserService userService; @Autowired PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Autowired MyAccessDecisionManager myAccessDecisionManager; @Autowired MyFilter myFilter; @Bean PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder () { return PasswordEncoderFactories.createDelegatingPasswordEncoder(); } @Override protected void configure (AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception auth.userDetailsService(userService).passwordEncoder(passwordEncoder); } @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.authorizeRequests().withObjectPostProcessor(new ObjectPostProcessor<FilterSecurityInterceptor>() { @Override public <O extends FilterSecurityInterceptor> O postProcess (O object) { object.setAccessDecisionManager(myAccessDecisionManager); object.setSecurityMetadataSource(myFilter); return object; } }) .and() .formLogin() .permitAll() .and().csrf().disable(); } }
Security JSON登录
通过阅读UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter源码,我们得知,Security是通过request请求得到Username的,这种形式经常在servlet出现,那也就是Security是能通过表单登录,而无法通过JSON登录,这样对前后端分离是不友好的
更改UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter,使其支持JSON登录,注意只是扩展功能,不是重写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class MyUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter extends UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter @Override public Authentication attemptAuthentication (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws AuthenticationException if (!request.getMethod().equals("POST" )) { throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod()); } if (request.getContentType().equals(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE)){ Map<String,String> map; try { map = new ObjectMapper().readValue(request.getInputStream(), Map.class); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod()); } String username = map.get("username" ); username = (username != null ) ? username : "" ; username = username.trim(); String password = map.get("password" ); password = (password != null ) ? password : "" ; System.out.println("JSON解析:" +username+":" +password); UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(username, password); setDetails(request, authRequest); return this .getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest); } return super .attemptAuthentication(request, response); } }
编写好自定的登录过滤器后,将其添加在UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter内部
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Configuration public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception ... http.addFilterAt(myAuthenticationFilter(),UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class); } MyUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter myAuthenticationFilter () throws Exception { MyUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter filter = new MyUsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter(); filter.setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManagerBean()); return filter; } }
Security整合WebSocket
文档参考:https://developer.aliyun.com/article/763747
https://blog.csdn.net/achenyuan/article/details/80851512#java-config配置
HTTP 协议是一种无状态的、无连接的、单向的应用层协议。它采用了请求/响应模型。通信请求只能由客户端发起,服务端对请求做出应答处理。这种通信模型有一个弊端:HTTP 协议无法实现服务器主动向客户端发起消息。
WebSocket 连接允许客户端和服务器之间进行全双工通信,以便任一方都可以通过建立的连接将数据推送到另一端。WebSocket 只需要建立一次连接,就可以一直保持连接状态。这相比于轮询方式的不停建立连接显然效率要大大提高。
点对面 (对所有在线的用户广播消息)
首先导入依赖,maven导入方便管理
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > sockjs-client</artifactId > <version > 1.5.1</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > jquery</artifactId > <version > 3.6.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > stomp-websocket</artifactId > <version > 2.3.4</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.webjars</groupId > <artifactId > webjars-locator-core</artifactId > <version > 0.47</version > </dependency >
WebSocket的配置类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Configuration @EnableWebSocketMessageBroker public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer @Override public void configureMessageBroker (MessageBrokerRegistry registry) registry.enableSimpleBroker("/topic" ); registry.setApplicationDestinationPrefixes("/app" ); } @Override public void registerStompEndpoints (StompEndpointRegistry registry) registry.addEndpoint("/chat" ).withSockJS(); } }
处理消息的Controller类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @Controller public class GreetingController @MessageMapping("/hello") @SendTo("/topic/greetings") public Message greeting (Message message) return message; } }
前端页面
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <script src ="/webjars/jquery/jquery.min.js" > </script > <script src ="/webjars/sockjs-client/sockjs.min.js" > </script > <script src ="/webjars/stomp-websocket/stomp.min.js" > </script > </head > <body > <table > <tr > <td > 请输入用户名</td > <td > <input type ="text" id ="name" > </td > </tr > <tr > <td > <input type ="button" id ="connect" value ="连接" > </td > <td > <input type ="button" disabled ="disabled" id ="disconnect" value ="断开连接" > </td > </tr > </table > <div id ="chat" style ="display: none" > <table > <tr > <td > 请输入聊天内容</td > <td > <input type ="text" id ="content" > </td > <td > <input type ="button" id ="send" value ="发送" > </td > </tr > </table > <div id ="conversation" > 群聊进行中....</div > </div > <script > $(function ( $("#connect" ).click( function ( connect() } ) $("#disconnect" ).click( function ( if (stompClient != null ){ stompClient.disconnect(); } setConnected(false ); } ) $("#send" ).click( function ( stompClient.send("/app/hello" ,{},JSON .stringify({"name" :$("#name" ).val(),"content" :$("#content" ).val()})) } ) } ) var stompClient =null ; function connect ( if (!$("#name" ).val()){ return ; } var socket=new SockJS("/chat" ); stompClient=Stomp.over(socket); stompClient.connect({},function (success ) setConnected(true ); stompClient.subscribe("/topic/greetings" ,function (msg ) showGreeting(JSON .parse(msg.body)); }); }) } function setConnected (flag ) $("#connect" ).prop("disabled" ,flag); $("#disconnect" ).prop("disabled" ,!flag); if (flag){ $("#chat" ).show(); }else { $("#chat" ).hide(); } } function showGreeting (msg ) $("#conversation" ).append("<div>" +msg.name+":" +msg.content+"</div>" ); } </script > </body > </html >
点对点 (将消息发送到指定用户上)
由于引入了用户的概念 ,导入 Security依赖
1 2 3 4 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId > </dependency >
配置点对点发送的请求路径
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 @Configuration @EnableWebSocketMessageBroker public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer @Override public void configureMessageBroker (MessageBrokerRegistry registry) registry.enableSimpleBroker("/topic" ,"/queue" ); registry.setApplicationDestinationPrefixes("/app" ); } @Override public void registerStompEndpoints (StompEndpointRegistry registry) registry.addEndpoint("/chat" ).withSockJS(); } }
点对点的Controller类
这里使用了SpringBoot的自动配置类 ,SimpMessagingTemplate消息模板,它可以指定用户发送
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 @Controller public class GreetingController @Autowired SimpMessagingTemplate messagingTemplate; @MessageMapping("/hello") @SendTo("/topic/greetings") public Message greeting (Message message) return message; } @MessageMapping("/one") public void one (Principal principal, Chat chat) chat.setFrom(principal.getName()); messagingTemplate.convertAndSendToUser(chat.getTo(),"/queue/greetings" ,chat); } }
前端页面
注意一旦使用点对点 就要在指定的发送路径上加上/user前缀!!!
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 <!DOCTYPE html > <html lang ="en" > <head > <meta charset ="UTF-8" > <title > Title</title > <script src ="/webjars/jquery/jquery.min.js" > </script > <script src ="/webjars/sockjs-client/sockjs.min.js" > </script > <script src ="/webjars/stomp-websocket/stomp.min.js" > </script > </head > <body > <table > <tr > <td > <input type ="button" id ="connect" value ="连接" > </td > <td > <input type ="button" disabled ="disabled" id ="disconnect" value ="断开连接" > </td > </tr > <tr > <td > 接送人</td > <td > <input type ="text" id ="toname" > </td > </tr > </table > <div id ="chat" style ="display: none" > <table > <tr > <td > 请输入聊天内容</td > <td > <input type ="text" id ="content" > </td > <td > <input type ="button" id ="send" value ="发送" > </td > </tr > </table > <div id ="conversation" > 群聊进行中....</div > </div > <script > $(function ( $("#connect" ).click( function ( connect() } ) $("#disconnect" ).click( function ( if (stompClient != null ){ stompClient.disconnect(); } setConnected(false ); } ) $("#send" ).click( function ( if (!$("#toname" ).val()){ return ; } stompClient.send("/app/one" ,{},JSON .stringify({"to" :$("#toname" ).val(),"content" :$("#content" ).val()})) } ) } ) var stompClient =null ; function connect ( var socket=new SockJS("/chat" ); stompClient=Stomp.over(socket); stompClient.connect({},function (success ) setConnected(true ); stompClient.subscribe("/user/queue/greetings" ,function (msg ) showGreeting(JSON .parse(msg.body)); }); }) } function setConnected (flag ) $("#connect" ).prop("disabled" ,flag); $("#disconnect" ).prop("disabled" ,!flag); if (flag){ $("#chat" ).show(); }else { $("#chat" ).hide(); } } function showGreeting (msg ) $("#conversation" ).append("<div>" +msg.from+":" +msg.content+"</div>" ); } </script > </body > </html >
报错
There is no PasswordEncoder mapped for the id “null”
该报错是因为我们在往数据库写入密码是没有加上BCryptPasswordEncoder特有的ID加密方式
在每一个经过BCryptPasswordEncoder加密的字符串都会有{id}
我们来看一下官方文档:
The general format for a password is:
{id}encodedPassword
这样,id是一个标识符,用于查找应该使用哪个PasswordEncoder,而encodedPassword是所选PasswordEncoder的原始编码密码。id必须在密码的开头,以{开头,密码}结尾。如果找不到id, 密码将为空。例如,下面可能是使用不同id编码的密码列表。所有原始密码都是“password”
{bcrypt}$2a$10$dXJ3SW6G7P50lGmMkkmwe.20cQQubK3.HZWzG3YB1tlRy.fqvM/BG
{noop}password
{pbkdf2}5d923b44a6d129f3ddf3e3c8d29412723dcbde72445e8ef6bf3b508fbf17fa4ed4d6b99ca763d8dc
{scrypt}$e0801$8bWJaSu2IKSn9Z9kM+TPXfOc/9bdYSrN1oD9qfVThWEwdRTnO7re7Ei+fUZRJ68k9lTyuTeUp4of4g24hHnazw==$OAOec05+bXxvuu/1qZ6NUR+xQYvYv7BeL1QxwRpY5Pc=
{sha256}97cde38028ad898ebc02e690819fa220e88c62e0699403e94fff291cfffaf8410849f27605abcbc0
解决方法
在数据库的密码字段上{id}的方式
尝试{bcrypt},{pbkdf2},{scrypt}